In this blog post, we will look in detail Ethereum 2.0 staking, staking pools and how they operate. As an example, I feature the StakeWise staking pool service and then explore the return on investment, risks and technical aspects of staking.
Ethereum 2.0 phase 0 chain launch is imminent. I expect the popularity of staking pools to increase quickly, as they are a convenient way for non-technical users to put their ETH capital in productive use.
What is Proof of Stake? #
Ethereum 2.0 is a long term upgrade plan for Ethereum 1.0, the most popular blockchain at the moment. Ethereum 2.0 will be a Proof of Stake blockchain. In a Proof of Stake consensus model the validators who ensure the blockchain gets new blocks and moves forward, stake some capital (ETH) to receive block production rewards.
Validator clients stake some capital (min 32 ETH), but the actual hardware can be modest. This is opposite to Bitcoin and Ethereum 1.0 where miners need to buy specialised physical mining devices and burn vast amounts of electricity to receive block rewards. In this sense, the Ethereum 2.0 network will be much more secure as there is going to be more operators ensuring the network security.
Validators ensure the Ethereum 2.0 network security. If a validator fails to produce good blocks on its turn, e.g. by being offline, they are penalised and lose rewards. If the validator acts dishonestly, does a so-called double attestation attack and is caught, the validator risks being slashed and losing its principal capital. More information about penalties in this article from Consensys.
Why Ethereum 2.0 will be a boon for staking pools? #
The first stage of Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is a so-called beacon chain that serves as the foundation of the new proof-of-stake upgrade over old proof-of-work.
The minimum capital requirement for running Ethereum 2.0 is 32 ETH (USD 15k as the writing of this). Besides minimum capital specialised IT operations knowledge is required to run the validation nodes efficiently. In the staking pools, a pool operator providers IT infrastructure and management whereas staking pool members provide the capital.
Furthermore, block rewards in Ethereum 2.0 are not consumable right away. ETH 1.0 will be 1:1 redeemable to ETH 2.0 in the future. But we do not know when because Ethereum 2.0 deployment roadmap is very complex spanning over several years. Thus, any capital locked for staking and its rewards will be locked for the foreseeable future.
Instead of directly staking, it is more capital safe to own shares through a staking pool membership. Shares present the principal of staked capital, current and future interest accrued for the pool. Staking pool shares are always transferable. You can cash out your staking position by selling your staking pool shares.
What is StakeWise? #
StakeWise is one of the staking pool services for Ethereum 2.0.
StakeWise team is based in Estonia, known for its crypto friendliness. StakeWise founding team is likewise Estonians, Dmitri Tsumak and Kirill Kutakov.

StakeWise is a smart contract-based service. The staking pool launches as a custodial pool but later plans to migrate to be completely non-custodial. Unlike centralised staking services like cryptocurrency exchanges, the tokenized shares in Stakewise pool are publicly tradable as ERC-20 tokens. This allows you to enter and exit otherwise illiquid ETH 2.0 staking positions. Furthermore, smart contracts ensure 100% transparency towards the service users making it harder for the operators to hide any issues.
Currently StakeWise is in a beta (testnet) mode and does not offer yet Ethereum 2.0 real staking. The best way to learn more about StakeWise is on their website and Discord.
In the future, StakeWise plans to decentralise ownership and operations as much as possible for a staking service, becoming a fully decentralised autonomous organisation (DAO). This will make Stakewise much less risky than centralised staking services, often offered by cryptocurrency exchanges like Binance and Kraken.
Competition in Ethereum 2.0 staking service space #
There is plenty of competition for Ethereum 2.0 staking services. Some notable competitors for StakeWise include AllNodes and Rocket Pool.
As a disclaimer, I do not have any association or relationship with StakeWise. I picked it solely for this post because the founders were friendly and approached me.
How much interest can you earn in Ethereum 2.0 staking? #
As discussed previously, those who stake are rewarded with block rewards that consist of ETH 2.0 inflation (network issuance) and later transaction fees when the Ethereum 2.0 network reaches phase 2.
Staking rewards for Ethereum 2.0 will depend on how much Ethereum is locked for staking. The max theoretical annual interest for your Ethereum will be between 1.8% - 22.9%. To achieve the theoretical interest your Ethereum 2.0 node must operate flawlessly. It is reasonable to expect some Ethereum 2.0 development hiccups, problems with the Internet and problems with server hardware that may cause this number to go down.
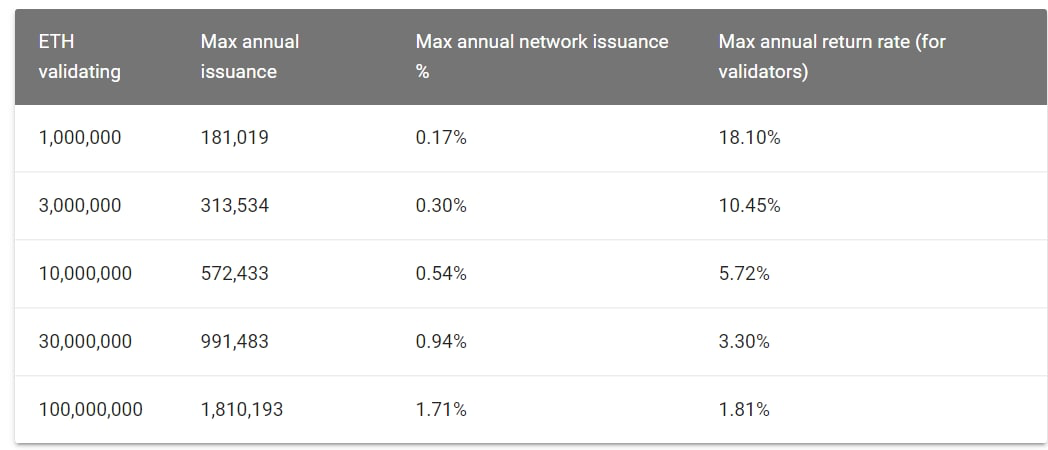
Ethereum 2.0 staking rewards table courtesy of EthHub.
For the clarity, this is not free interest - there has to be a server somewhere doing the work for the network with access to staking capital.
How does Ethereum 2.0 staking work? #
In Ethereum 2.0 network operation is divided between beacon nodes and validator clients. A detailed overview can be found in EthHub documentation.
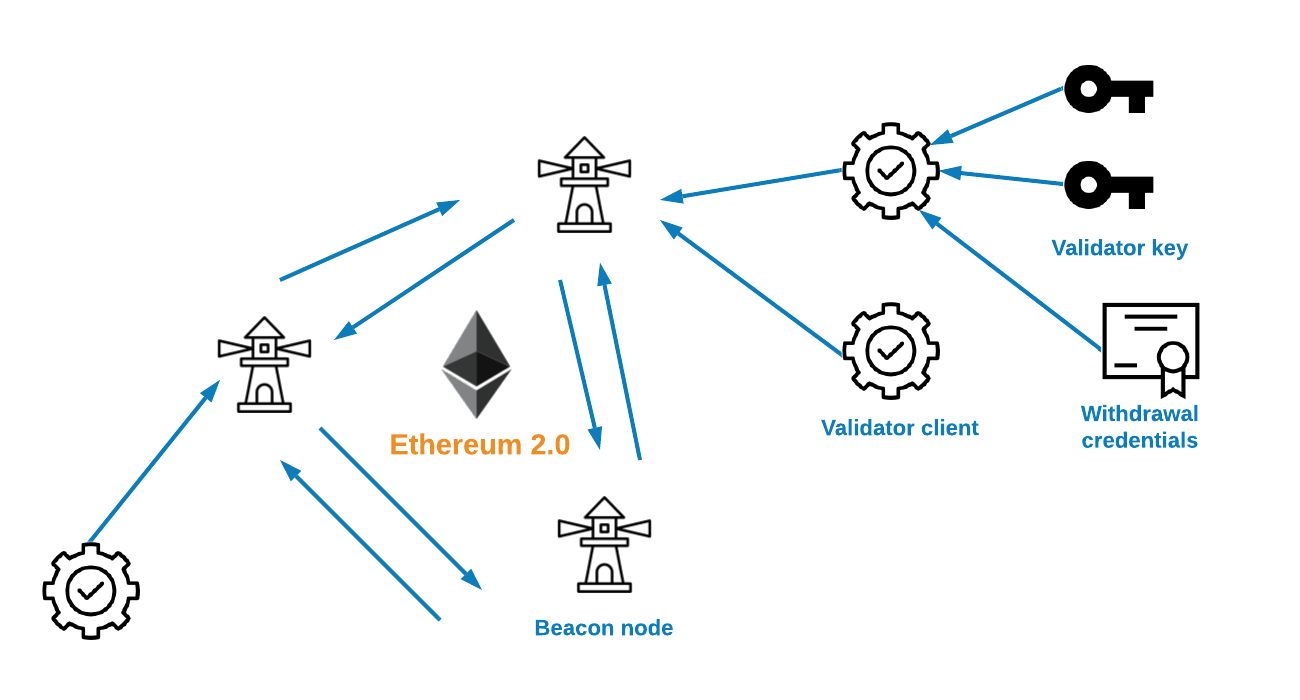
- Beacon nodes are somewhat similar to Ethereum 1.0 full nodes and are responsible for forming the peer-to-peer network of transactions. Beacon nodes also process attestations from validator clients. Beacon nodes do not do staking themselves.
- Validator clients are a little bit like miners. One validator client connects to a single beacon node. A validator client needs to have a minimum of 32 ETH assigned to it to participate in the block creation process and receive block rewards.
- One validator client can have multiple stakes, also known as validation keys, assigned to it. There is no need to have a separate physical server process for every new 32 ETH staked.
To bootstrap the staking network, ETH 1.0 can be deposited in Ethereum 2.0 Deposit Contract. This ETH becomes permanently locked and staked until Ethereum 2.0 network has reached maturity to do transfers. Any accrued Ethereum 2.0 staking rewards are accounted for by an Ethereum 2.0 public key, represented by _withdrawal credentials _in the deposit contract. Anyone who controls the withdrawal credential keys has full control over ETH when the Ethereum 2.0 gets there.
How are staking pools better than staking yourself? #
The staking interest is nominated in ETH, not a US dollar. ETH value, as being a cryptocurrency, is volatile and can swing as much as 80% over medium periods of time.
If ETH value makes large swings, for example down 80% and then up 80%, over the next three years then it is better to sell at the top and buy at the bottom instead of directly tying up your ETH capital to staking. Or simply exit your position of holding ETH if there is a larger downtrend, or bear market, in progress.
Because staked ETH cannot be moved yet, you will tie up your capital during the bear market if you decide to stake solo. You can mitigate this with a staking pool. Instead of directly staking your ETH yourself, you use your ETH to deploy your capital through a staking pool. Then the staking pool will stake with your ETH inflow. Alternatively, if someone wants to exit the staking pool you can buy shares at a discount for the underlying value that is staked ETH and received block rewards.
Staking pool shares are also likely to be good collateral in decentralised finance services like Aave or MakerDAO. Instead of exiting your position in staking with a hit, you can take a loan against your staking pool shares and wait for the market to recover.
How does staking with StakeWise work? #
StakeWise offers two staking modes: pool and solo.
Pool mode #
In a pool mode, you contribute your ETH towards a StakeWise staking pool that stakes with all pooled ETH.
You deposit into the pool smart contract and receive pool shares as ERC-20 tokens in return. The pool then will deposit this ETH to Ethereum 2.0 Deposit Contract.
There are two tokens.
- Staked ETH (stETH) reflect 1:1 ETH pool deposited in Ethereum 2.0 Deposit contract.
- Reward ETH (rwETH) reflects accrued staking rewards and will be proportionally distributed to the pool members.
For each new 32 ETH deposited to the pool contract, StakeWise allocates a new validator client key and then may also spin up a new validator client in their cloud service infrastructure.
StakeWise the corporation takes a 10% cut on staking rewards for maintaining its service, that consists of a website (frontend), cloud service infrastructure (backend) and smart contracts. There are no fees on deposits.
Though the pool service is smart contract based, you still rely on StakeWise to run the server infrastructure to generate profits for the pool. Any losses due to validation client errors during the staking will be absorbed by the pool as a whole.
Solo mode #
In a StakeWise solo mode, for $10/month, you can assign your withdrawal credentials for a validator client run by StakeWise. The minimum of 32 ETH deposit is required. There are no other fees.
StakeWise is renting the server, when needed, behind the scenes from a cloud service provider. StakeWise will manage the server failover, in the case underlying physical server breaks, your validator will have an automatic failover transition to a new server.
Differences between solo and pool modes are
- In solo mode, the user providers withdrawal credentials themselves. The withdrawal credentials represent hash of the withdrawal public key, that will have the control over funds in ETH 2.0
- In the future, the user may be able to move staked ETH 2.0 between different validators with their withdrawal credentials
- In solo mode, the validator client cost is directly billed from the user as a flat $10 fee whereas in the pooled mode this is taken from the pool profits
How can you trade StakeWise staking pool shares? #
If you want to exit the staking pool early you can try to find a buyer for your pool shares. This is the main benefit over staking solo - your capital is not locked up until Ethereum 2.0 matures.
I expect to see several market places for staked ETH shares, run internally by StakeWise and other services. Then these staking pool shares can be swapped 1:1 on a Curve pool or similar, as even though the staking pool shares present rights under different operators, the underlying asset and mechanisms are the same across all staking pool operators.
In theory, major staking pool shares should closely follow the ETH price. There will be minor discounts for operator counterparty risk, technical risk related to ETH 2.0 launch and more illiquid markets.
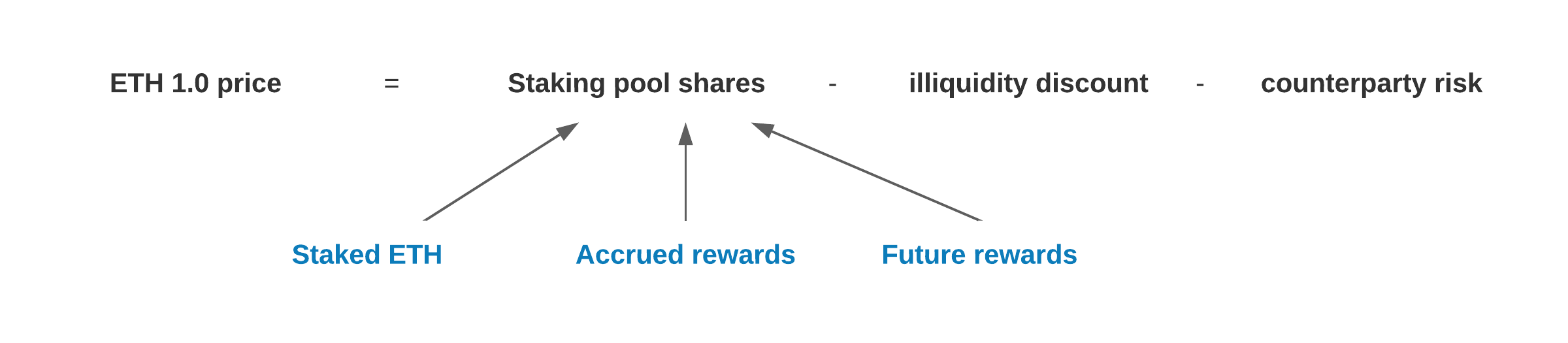
How can you redeem ETH 2.0 when it is ready? #
Eventually, the ETH 2.0 block rewards, tokenised by StakeWise smart contracts as rwETH token, can be accessed and moved to your Ethereum 2.0 account.
When Ethereum 2.0 the redemption of staking pool shares happens by burning stETH and rwETH, having the sufficient number of validators to exit and then transferring ETH 2.0 to the address given by the holder of the tokens.
Technical analysis of StakeWise smart contracts and infrastructure #
In this section, I dissect StakeWise smart contracts and infrastructure more in detail. The information here is mostly useful for hedge funds doing risk analysis and to understand what they commit into when putting their ETH in StakeWise pool. It is also useful for other Ethereum developers and integrators who want to integrate StakeWise pool shares in their services.
A good Ethereum 2.0 staking model description can be found in this article from Attestant. An overview of StakeWise smart contracts is available in StakeWise documentation. StakeWise has very good technical documentation and their smart contracts are well structured, making them a joy to explore and read.
For the simplification, we discuss only the pooled mode of StakeWise staking. Note that the risks here are not specific to StakeWise business model, but shared between all Ethereum 2.0 staking pool operators.
How do StakeWise validator client and beacon node infrastructure operate? #
StakeWise use a Kubernetes cluster that hosts multiple beacon nodes for Ethereum 2.0 for redundancy and validator clients that connect to the beacon nodes for getting tasks from them. All of them run in docker containers.
How are deposits handled? #
- The user deposits ETH to Pool
- The user receives an equal amount of stETH in return
Then later
- The operator calls registerValidator to assign collected 32 ETH to a new validator key
- Validator public key is registered in the smart contract mapping
- The ETH is forwarded from the pool contract to ETH 2.0 deposit contract
How are withdrawals handled? #
ETH 2.0 withdrawals won’t be available until the far future.
- All validator keys in the pool share the same withdrawal credentials
- These credentials are controlled by StakeWise, using multiparty computing, in a multisignature manner
Ethereum community is working to have a safer way to address ETH 2.0 withdrawals and support withdrawals to ETH 1.0 addresses (smart contracts and normal ones).
How are validator clients and StakeWise smart contracts connected? #
The operator generates new validator keys for each 32 ETH assigned to the pool - withdrawal credentials are the same for the whole pool.
What centralised control StakeWise has over smart contracts? #
StakeWise includes some master keys for the smart contracts. These include
Can StakeWise steal or lose deposited ETH? #
Currently, there is no visibility of withdrawal credential handling process. StakeWise could lose withdrawal credential keys to an external attacker or there could be an insider fraud.
This can be mitigated in the future by having more diverse and robust base of keyholders and cosigners, as discussed later.
Can StakeWise manipulate staked ETH (stETH) shares? #
StakeWise can unilaterally upgrade the token contract and thus manipulate balances. However this would be immediately obvious to everyone.
Risks of having validator keys exposed #
Currently Ethereum 2.0 does not allow cycling the validator keys. This may be changed in the future versions.
If StakeWise has the validator keys compromised, for example through a malicious cloud service operator, then an attacker can force slashing of validators, leading to the loss and burning of the staked ETH. Though destroying capital itself is not that interesting, the attacker could blackmail StakeWise for ransom or start slashing validators. But validators clients can exit from the staking process in 1-2 days, so the risk for doing harm through validator keys is quite small.
Risks of having issues running validator clients #
Validator nodes should stay online, although Ethereum 2.0 staking contracts are very flexible. In the case of StakeWise, risks include infrastructure problems by StakeWise cloud server provider, StakeWise human errors or problems with the Ethereum 2.0 itself. However, the risk of losing capital this way is small, because only new block rewards can be lost.
Risks of the resiliency of the beacon node network #
Any beacon node needs to accept TCP/IP traffic. There is a raw IP denial-of-service attack scenario where the attacked can try to take StakeWise beacon nodes offline.
In this case, StakeWise validator clients would stop validating, but no stETH is lost. If validators are offline for a long time, pool earnings are affected. This risk is quite easily migrated by having multiple spare cloud operators ready to go.
Risks of StakeWise becoming non-operational #
There are few scenarios that would be very harmful for StakeWise users
- StakeWise key team members become non-operational (so-called hit-by-a-bus scenario)
- StakeWise key team members have in internal conflict and one or few team members can make the company effectively non-operational due to a grudge
- StakeWise company is going to the administration, but winds up cleanly and all assets are transferred or sold before administration
- StakeWise company bankrupts uncleanly, the service agreement with IT and key management services are terminated and keys are lost
Team member scenarios can be mitigated with independent directors who oversee company private matters and can intervene. Bankruptcy and wind up scenarios can be mitigated with plans and contracts that guarantee the safe transfer of critical assets to a third party that can take over in the case of a non-operational situation.
Later on, new Ethereum 2.0 features can further allow more decentralisation for StakeWise users who then need to rely less on the operator.
How to improve staking pool security #
As discussed before, some of the staking pool actions must be centralised to operators, some can be decentralised and in the future hopefully decentralised even more with the upcoming upgrades to Ethereum 2.0 protocol.
There are few actions how StakeWise and other Ethereum staking pool operators could improve its security best practices and offer staking pool users better assessment of risk. The list is based on the best practices that industry regulators are looking for in cryptocurrency companies where custodial companies need to have a license. These include e.g.
- Transparency on the list of critical keys and how they are managed
- Transparency of who are the key holders
- Documented best practises critical key access
- Third party audit of key management practices with some penetration testing
- Including non-executive director like keyholders, diverse key holdership and increase the number of key holders
- Plan to migrate future stakes to ETH 1.0 withdrawal addresses when support is available
- Wind up a plan and contracts to transfer/sell StakeWise critical assets to a third party who can take over, in the case company becomes inoperational e.g. due to running out of money, losing multiple key members at the same time or some geopolitical disruption
Conclusion #
Ethereum 2.0 staking pools are coming. Pooled staking and staking pool shares as ERC-20 tokens is practical for many DeFi users and probably the direction where Ethereum community is heading. StakeWise as an operator is technically very competent, open for discussion and improvements. Currently there are many benefits to stake through a pool over centralised services and in the future there will be even more.

Comments
Send any feedback and comments by replying the Twitter thread.
Discuss